pleural effusion cat ultrasound
Accumulation of fluid in the pleural space. Measurement of a pleural effusion volume with point-of-care ultrasonography may be a useful tool for intensivists and is an active area of research in critical care 7.

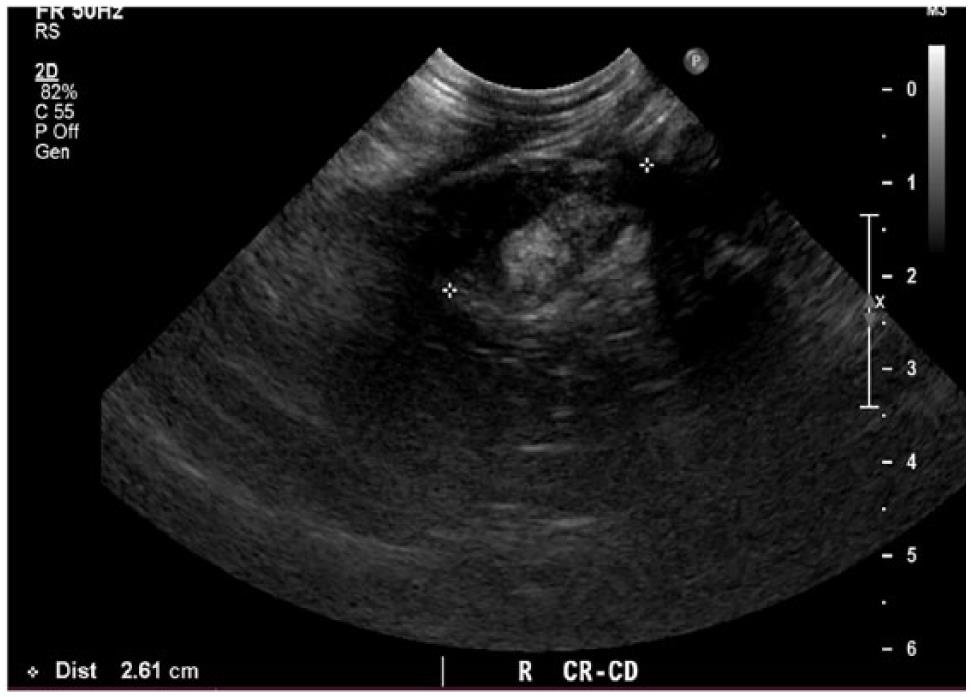
Fig Ure 3 Abdominal Ultrasound Images Of A 9 Year Old Cat Case 4 With Download Scientific Diagram
Cats with pleural effusion often have rapid shallow breathing and pet owners may notice increased respiratory effort.

. This review outlines a practical approach to cases of pleural effusion focusing on early recognition and confirmation of pleural space disease stabilisation of the. Sitting or lying in strange positions to ease breathing. For those who are new to imaging around the heart with ultrasound differentiating a pericardial from a pleural effusion can be tricky particularly when the pleural effusion is circumferential around the heart.
Feline infectious peritonitis. Blood NTproBNP LUS and FCU evaluating left atrial LA size and presence of pericardial effusion PCEFF were performed in all cats. Examination of the effusion included determination of specific gravity using a refractometer Atago Company as well as measurement of the total cell count with the Cell-Dyn 3500 System Abott Laboratories.
Collection of pleural effusion was performed by blind or ultrasound-guided thoracentesis. Unlike with a pericardial effusion in the case of accumulation of fluid in the pleural space there is no collapse of the heart walls. This non-invasive and quick test can help the veterinarian evaluate the cat quickly.
Some affected cats may also cough. Pleural fluid is often represented as a hazy opacity of one hemithorax with preserved vascular shadows. This review outlines a practical approach to cases of pleural effusion focusing on early recognition and confirmation of pleural space disease stabilisation of the patient and logical diagnostic investigation.
Given that most effusions are detected by x-ray which generally cannot distinguish between fluid types the fluid in. Pleural effusion or pericardial effusion can cause muffled heart sounds. Diagnostics will be necessary to confirm the cat has pleural effusion and determine a cause.
Pleural effusions can be entirely overlooked on supine radiographs or can be misdiagnosed as pulmonary consolidation or atelectasis. Cats presenting with pleural effusion are nearly always in respiratory distress ranging from an increased respiratory rate and effort to open mouth breathing. This can be caused by thoracic lymphangiectasia swollen lymph vessels that leak chyle into the pleural space congestive heart failure obstruction of the cranial vena cava the major vein that returns blood to the heart from the front of the body cancer fungal infection feline heartworm.
Tumors in the lungs or chest wall can lead to pleural effusion. Determining the underlying aetiology is key to appropriate management. Focused Assessment Sonography for Trauma FAST procedure.
When a cat is suffering from pleural effusion the liquid present in the chest cavity prevents the lungs from fully inflating. In the latter situations therapeutic intervention must be initiated quickly to prevent respiratory arrest. In the below clip from the Sonoscape S2 you can actually see the separation of the right ventricular free wall from the pericardium in a cat.
Lung ultrasound findings including pleural effusion PLEFF number of Blines and subpleural abnormalities were noted. In some cats infection with mutated coronavirus can lead to blood vessel damage which results in fluid leakage. When FIP affects the chest cavity pleural effusion results.
In the following article we present two cases concluding with a third case in which both types of effusion can be seen simultaneously. The most commonly diagnosed cause of pleural effusion in cats is chylothorax. Pleural effusion is typically.
Other signs are loss of sharp silhouette of the ipsilateral hemidiaphragm and thickening of the minor fissure. A cat with this condition might show some or all of the following signs. Rishniw M Weidman J Hornof WJ Hydrothorax secondary to a perinephric pseudocyst in a cat.
Diverse disease processes result in sufficient fluid accumulation within the pleural space to cause respiratory compromise. Cats may develop open-mouthed breathing in an effort to increase air flow. There are a number of characteristic findings on radiographs that will help your veterinarian identify the presence of pleural effusion.
Screening for effusions can be. Found with right congestive heart failure obstruction to lymphatic drainage by tissue adhesions in pleural space lung lobe torsion neoplasms and abdominal contents herniating. Determining the underlying aetiology is.
Abdominal ultrasounds were performed in 70 cats with pleural effusion and revealed concurrent abdominal effusion in 59 of these cats. In controlled settings ultrasound may detect constitutive pleural fluid can reliably detect effusions 20 mL in clinical settings and may approach the sensitivity and specificity of computed tomography. Vet Radiol Ultrasound 1998.
There is no published method to reliably quantify pleural fluid volume in cats although methods are. Pleural effusion is commonly used as a catch-all term to describe any abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity. This syndrome is caused by infection with a mutated form of a feline coronavirus.
Pleural effusion can be confirmed with radiography a single DV view if patient permits or thoracic ultrasonography. Pleural effusion in cats with pyothorax in. Ultrasound is widely considered to be more sensitive than radiography to the presence of pleural effusion in man but this has not so far been reported in cats or dogs1 2 3 It is also often used to subjectively monitor fluid volume in cases of chronic effusion.
Four standard effusion types recognized in addition to blood. The lack of specificity is mainly due to the limitations of the imaging modality. Pleural effusion can have a number of different causes including diseases of the heart lungs or other systemic diseases.
Signs of Pleural Effusion in Cats. Diverse disease processes result in sufficient fluid accumulation within the pleural space to cause respiratory compromise. Pleural effusion is typically diagnosed by taking radiographs X-rays of the chest.
Major Differential Diagnoses for Pleural Effusion in the Cat. Abdominal abnormalities identified on ultrasound included abdominal masses lymphadenopathy hepatic venous congestion hepatomegaly splenomegaly renal enlargement small intestinal wall thickening steatitis and pancreatitis. In some cases ultrasound may also be.
The therapeutic intervention also provides your first diagnostic test. Medical records were evaluated for final diagnosis. A chest ultrasound to look for the presence of fluid within the pleural cavity.

Cardioechography Sonography Student Ultrasound School Ultrasound Physics

Abdominal Ultrasound Images Of A 5 Year Old Cat Case 1 With An Download Scientific Diagram

Pin By Sal Thompson On Radiography Medical Ultrasound Vision Eye Radiography

Pdf Thoracic Ultrasound A Method For The Work Up In Dogs And Cats With Acute Dyspnea Semantic Scholar
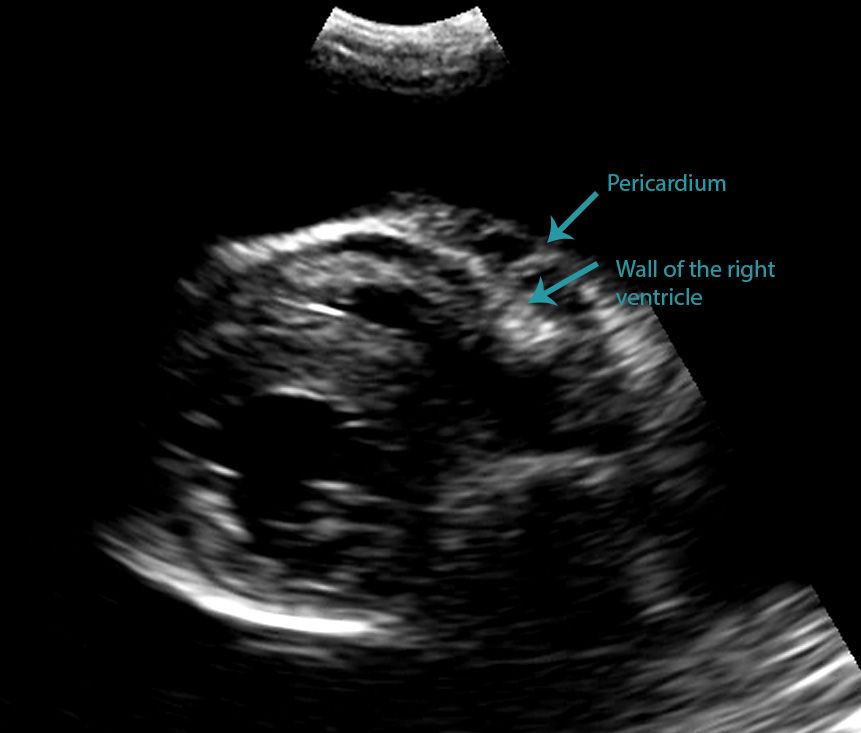
Veterinary Echocardiography Newsletter 1 Effusions Animal Ultrasound Association
Ultrasound Guided Lung Biopsy Vet Practice Support
Animals Free Full Text Lung Ultrasound For Imaging Of B Lines In Dogs And Cats A Prospective Study Investigating Agreement Between Three Types Of Transducers And The Accuracy In Diagnosing Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema

Utility Of Point Of Care Lung Ultrasound For Monitoring Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema In Dogs Murphy 2021 Journal Of Veterinary Internal Medicine Wiley Online Library
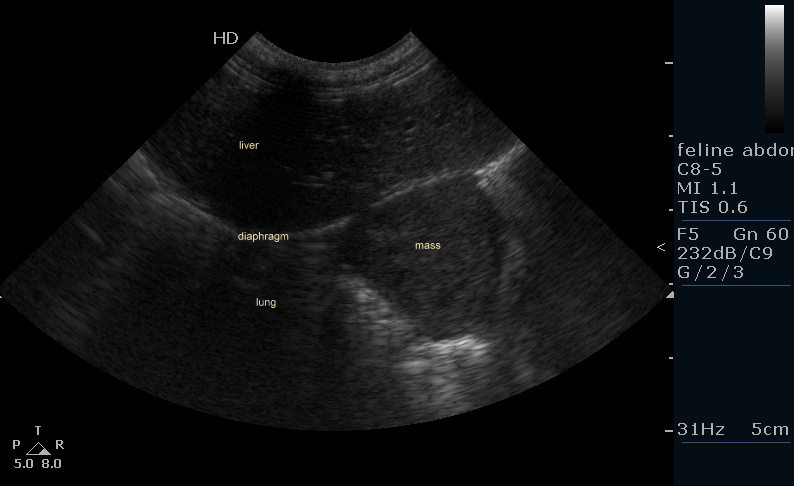
Spontaneous Cholecystopleural Fistula Leading To Biliothorax And Sepsis In A Cat

Differentiating Pericardial From Pleural Effusion Animal Ultrasound Association
Front Line Ultrasound Imaging Of The Feline Urinary

Cat Of Figure 1 Thoracic Ultrasound Revealed A Mild Hypoechoic Download Scientific Diagram

Fig Ure 2 Abdominal Ultrasound Images Of A 6 Year Old Cat Case 3 With Download Scientific Diagram
Lung Ultrasound Flooding In Fulminant Pulmonary Oedema In Cats And A Comparison With Pneumonia Vet Practice Support

Differentiating Pericardial From Pleural Effusion Animal Ultrasound Association

Focused Ultrasound Of Superficial Soft Tissue Swellings Masses And Fluid Collections In Dogs And Cats Veterinary Clinics Small Animal Practice

Pleural Effusion In A Cat Ultrasound Fip Youtube

Veterinary Echocardiography Newsletter 1 Effusions Animal Ultrasound Association